javascript의 깊은 복사
Javascript의 깊은 복사
javascript에서 primitive type은 값이 복사되어 전달되는
call by value형식을 따른다.하지만, 객체 타입은 값이 복사되어 전달되는 것이 아닌
객체가 저장되어 있는 '메모리 주소'에 대한 참조 값이 저장된다.
얕은 복사?
1
2
let user = { name: "joonamin", ...생략... }
let developer = user
앞 서 기술한 것 처럼, user 는 실제 값이 할당된 영역에 대한 참조 값을 저장한다.
하지만, 특정 function 내에서 side effect 없이 객체가 가진 ‘값’ 자체를 복사하기 위해서는 deep copy가 필요하다.
깊은 복사
javascript 진영에서는 과거까지만해도, 깊은 복사를 위한 객체 복제 내장 메소드 를 지원하지 않았다.
비교적 최근에는 structuredClone() 메소드를 제공해주는데, 이 방식이 등장하기 이전에는 어떠한 방식으로 깊은 복사를 구현하였는지 궁금하였다.
가장 단순한 방법
for 기반의 값 복사
1
2
3
4
5
6
let user = { name: "joonamin", ... 생략 ... }
let clonedUser = {}
for (let key in user) {
clonedUser[key] = user[key]
}
기존 객체의 프로퍼티들을 순회하며 primitive 수준까지 프로퍼티를 잘게 쪼개어 복사하는 방식이다.
가장 단순하지만, 중첩된 객체들을 처리하기 위한 추가적인 로직이 필요하다.
Object.assign(dst, [src, ...])
1
2
3
4
5
let user1 = { name: "joonamin1", ... 생략 ... }
let user2 = { name: "joonamin2", ... 생략 ... }
let clonedUsers = {}
Object.assign(clonedUser, user1, user2)
위 방식 또한, for 기반의 값 복사 형식으로 수행된다. 병합되는 src 들이 모두 primitive 수준이라면 for 기반의 값 복사 방식 보다 짧은 코드 라인 수로 간단하게 작성이 가능하다. (이는 전개 연산자 (...) 또한 마찬가지!)
하지만, 특정 property가 중첩 객체의 형식을 가진다면 여전히 얕은 복사가 가진 문제점들을 해결할 수 없다.
직렬화 & 역직렬화
1
2
const obj = /* ... */
const copy = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj))
직렬화 가능한 object를 직렬화 처리한 다음, 이를 다시 역직렬화 하는 방식이다.
이 방식은 serializable한 object에 대해서만 제약조건하에서 동작한다.
하지만, 위의 접근법은 흔히 우리가 접할 수 있는 cyclic한 object에 대해서는 적용할 수 없다는 단점이 있다.
1
2
3
4
const x = {}
const y = {x}
x.y = y // cycle: x.y.x.y.x.y.x...
const copy = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(x)) // throws
또한, Maps, Sets, RegExps, Dates 같은 built-in 타입은 serialize 단계에서 정보 유실이 발생할 수 있으므로 주의해야한다.
Structured Clone
- 하나의 영역에서 다른 영역으로 데이터를 보내기 위한 알고리즘
- cyclic한 object와 다양한 built-in type을 지원해준다는 장점
- 현재는 多 브라우저에서 deep copy를 위한 structured clone을 지원해줌
MessageChannel을 이용한 Structured Clone
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
class Cloner {
constructor() {
this.pendingClones = new Map()
this.nextKey = 0
const channel = new MessageChannel()
this.inPort = channel.port1
this.outPort = channel.port2
this.outPort.onmessage = ({data: {key, value}}) => {
const resolve = this.pendingClones.get(key)
resolve(value)
this.pendingClones.delete(key)
}
this.outPort.start()
}
cloneAsync(value) {
return new Promise(resolve => {
const key = this.nextKey++
this.pendingClones.get(key, resolve)
this.inPort.postMessage({key, value})
})
}
}
const structuredCloneAsync = window.structuredCloneAsync =
Cloner.prototype.cloneAsync.bind(new Cloner)
const main = async () => {
const original = {date: new Date(), number: Math.random()}
original.self = original
const clone = await structuredCloneAsync(original)
// nested object에 대한 deep copy 확인
console.assert(original !== clone)
console.assert(original.date !== clone.date)
// cyclic한 object에 대해서도 deep copy 여부 확인
console.assert(original.self === original)
console.assert(clone.self === clone)
// value의 동등성 확인
console.assert(original.number === clone.number)
console.assert(Number(original.date) === Number(clone.date))
console.log('assertions complete')
}
main()
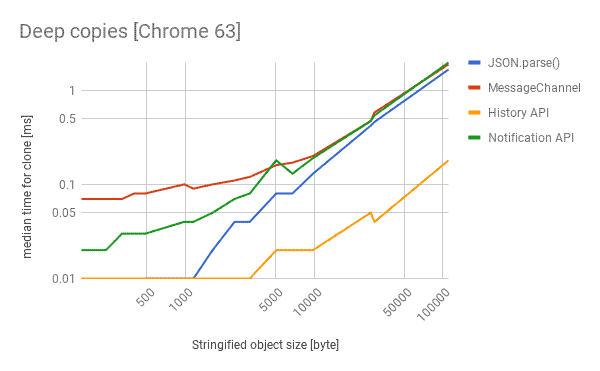
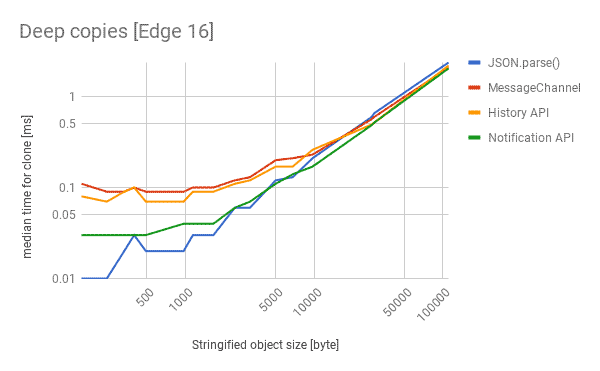
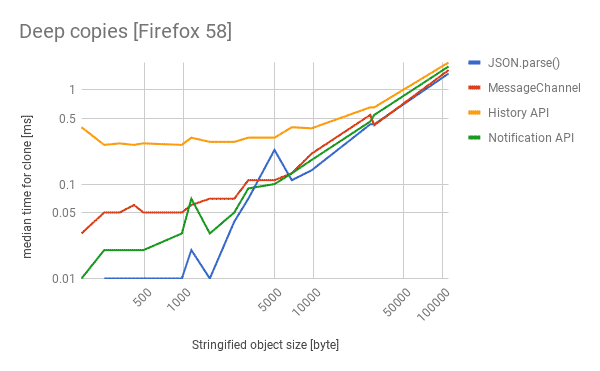
browser간 MessageChannel을 이용한 방식으로 serialzation algorithm을 사용한다. 이벤트 기반의 동작이므로 cloning 또한 asynchronous하다는 특징이 있다.
history API를 이용한 방식
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
const structuredClone = obj => {
const old = history.state
history.replaceState(obj, null)
const clonedObj = history.state
history.replaceState(old, null)
return clonedObj
}
browser의 history API를 사용한 방식은 synchronous 하게 동작하며, browser의 history를 임시 공간으로 활용하여 deep copy를 수행한다.
다만, history API는 cost가 큰 연산이므로 브라우저의 응답성을 떨어뜨릴 수 있다는 단점이 존재한다.
Notification API를 이용한 방식
1
2
3
4
5
const structuredClone = obj => {
const n = new Notification("", {data: obj, silent: true})
n.onshow = n.close.bind(n)
return n.data
}
browser의 notification API를 활용한 방식이다. notification에 대한 permission을 요구하고 허가 되지 않을 경우 실패한다는 단점이 존재한다.
–